Linux 用户管理-用户添加
发布于:2014-8-12 8:39 作者:admin 浏览:2332 分类:Linux1、 用户管理
Linux是个多用户多任务的分时操作系统,所有一个要使用系统资源的用户都必须先向系统管理员申请一个账号,然后以这个账号的身份进入系统。用户的账号一方面能帮助系统管理员对使用系统的用户进行跟踪,并控制他们对系统资源的访问;另一方面也能帮助用户组织文件,并为用户提供安全性保护。每个用户账号都拥有一个惟一的用户名和用户口令。用户在登录时键入正确的用户名和口令后,才能进入系统和自己的主目录。
实现用户账号的管理,要完成的工作主要有如下几个方面:
a.用户账号的添加、删除和修改。
b.用户口令的管理。
c.用户组的管理。
用户账号的管理主要涉及到用户账号的添加、删除和修改。
1.1 用户添加
添加用户账号就是在系统中创建一个新账号,然后为新账号分配用户号、用户组、主目录和登录Shell等资源。刚添加的账号是被锁定的,无法使用。
1、添加新的用户账号使用useradd命令,语法如下:
useradd [-d home] [-s shell] [-c comment] [-m [-k template]] [-f inactive] [-e expire ] [-p passwd] [-r] name
useradd 选项 用户名
Options:
-b, --base-dir BASE_DIR base directory for the home directory of the new account
-c, --comment COMMENT GECOS field of the new account comment (指定一段注释性描述)。
-d, --home-dir HOME_DIR home directory of the new account (指定用户主目录)
-D, --defaults print or change default useradd configuration (默认)
-e, --expiredate EXPIRE_DATE expiration date of the new account (自 1/1/1970 起,密码被修改的天数,指定账号的有效期限,缺省表示永久有效 )
-f, --inactive INACTIVE password inactivity period of the new account (指定在密码过期后多少天即关闭该账号)
-g, --gid GROUP name or ID of the primary group of the new account (指定用户所属的用户组)
-G, --groups GROUPS list of supplementary groups of the new account (指定用户所属的附加组)
-h, --help display this help message and exit (帮助)
-k, --skel SKEL_DIR use this alternative skeleton directory
-K, --key KEY=VALUE override /etc/login.defs defaults
-l, --no-log-init do not add the user to the lastlog and faillog databases
-m, --create-home create the user's home directory (如果此目录不存在,则同时使用-m选项,能创建主目录)
-M, --no-create-home do not create the user's home directory (不创建用户目录)
-N, --no-user-group do not create a group with the same name as the user (不创建组)
-o, --non-unique allow to create users with duplicate (non-unique) UID (重复UID)
-p, --password PASSWORD encrypted password of the new account (设置密码)
-r, --system create a system account (创建一个系统用户)
-s, --shell SHELL login shell of the new account (指定用户登入后所使用的shell)
-u, --uid UID user ID of the new account (需要说明的是,设定ID值时尽量要大于500,以免冲突。因为Linux安装后会建立一些特殊用户,一般0到499之间的值留给bin、mail这样的系统账号)
-U, --user-group create a group with the same name as the user (附加组)
-Z, --selinux-user SEUSER use a specific SEUSER for the SELinux user mapping (SEUSER用户)
范例1: useradd demouser1
建立用户名=demouser1(uid=503), 用户组=demouser1(gid=503), 用户目录=/home/demouser1, SHELL=/bin/bash ,密码=''
demouser1:x:503:503::/home/demouser1:/bin/bash (/etc/passwd)
demouser1:x:503: (/etc/group)
demouser1:!!:16113:0:99999:7::: (/etc/shadow)
范例2: useradd -d /var/loguser -m -g log -G root,www -s /sbin/nologin -u 555 -p 123456 -c '我是一个LOG管理员' -e 20000 -f 7
loguser:x:555:505:我是一个LOG管理员:/var/loguser:/sbin/nologin (/etc/passwd)
log:x:505: (/etc/group)
root:x:0:root,loguser (/etc/group)
www:x:501:loguser (/etc/group)
loguser:123456:16113:0:99999:7:7:20000: (/etc/shadow)
CSS兼容性3
发布于:2014-7-30 19:08 作者:admin 浏览:2063 分类:CSS例如:(其中floatA、floatB的属性已经设置为float:left;) <#div id=”floatA” ></#div>
<#div id=”floatB” ></#div>
<#div id=”NOTfloatC” ></#div>这里的NOTfloatC并不希望继续平移,而是希望往下排。
这段代码在IE中毫无问题,问题出在FF。原因是NOTfloatC并非float标签,必须将float标签闭合。
在 <#div class=”floatB”></#div>
<#div class=”NOTfloatC”></#div>之间加上 <#div class=”clear”></#div>这个div一定要注意声明位置,一定要放在最恰当的地方,而且必须与两个具有float属性的div同级,之间不能存在嵌套关系,否则会产生异常。
并且将clear这种样式定义为为如下即可: .clear{
clear:both;}此外,为了让高度能自动适应,要在wrapper里面加上overflow:hidden;
当包含float的box的时候,高度自动适应在IE下无效,这时候应该触发IE的layout私有属性用zoom:1;可以做到,这样就达到了兼容。
例如某一个wrapper如下定义: .colwrapper{
overflow:hidden;
zoom:1;
margin:5px auto;}
3、关于容器的包涵关系
很多时候,尤其是容器内有平行布局,例如两、三个float的div时,宽度很容易出现问题。在IE中,外层的宽度会被内层更宽的div挤破。一定要用Photoshop或者Firework量取像素级的精度。
4、关于高度的问题
如果是动态地添加内容,高度最好不要定义。浏览器可以自动伸缩,然而如果是静态的内容,高度最好定好。(似乎有时候不会自动往下撑开,不知道具体怎么回事)
5、最狠的手段 - !important;
如果实在没有办法解决一些细节问题,可以用这个方法.FF对于”!important”会自动优先解析,然而IE则会忽略.如下 .tabd1{
background:url(/res/images/up/tab1.gif) no-repeat 0px 0px !important; /*Style for FF*/
background:url(/res/images/up/tab1.gif) no-repeat 1px 0px; /* Style for IE */}值得注意的是,一定要将xxxx !important 这句放置在另一句之上,上面已经提过
IE7.0出来了,对CSS的支持又有新问题。浏览器多了,网页兼容性更差了,疲于奔命的还是我们 ,为解决IE7.0的兼容问题,找来了下面这篇文章:
现在我大部分都是用!important来hack,对于ie6和firefox测试可以正常显示,但是ie7对!important可以正确解释,会导致页面没按要求显示!搜索了一下,找到一个针对IE7不错的hack方式就是使用“*+html”,现在用IE7浏览一下,应该没有问题了。
现在写一个CSS可以这样:
#example { color: #333; } /* Moz */
* html #example { color: #666; } /* IE6 */
*+html #example { color: #999; } /* IE7 */
那么在firefox下字体颜色显示为#333,IE6下字体颜色显示为#666,IE7下字体颜色显示为#999.
关于CSS对各个浏览器兼容已经是老生常谈的问题了, 网络上的教程遍地都是.以下内容没有太多新颖, 纯属个人总结, 希望能对初学者有一定的帮助.
一、CSS HACK以下两种方法几乎能解决现今所有HACK.
1, !important
随着IE7对!important的支持, !important 方法现在只针对IE6的HACK.(注意写法.记得该声明位置需要提前.)
<style>
#wrapper
{
width: 100px!important; /* IE7+FF */
width: 80px; /* IE6 */
}
</style>
2, IE6/IE77对FireFox
*+html 与 *html 是IE特有的标签, firefox 暂不支持.而*+html 又为 IE7特有标签.
<style>
#wrapper
{
#wrapper { width: 120px; } /* FireFox */
*html #wrapper { width: 80px;} /* ie6 fixed */
*+html #wrapper { width: 60px;} /* ie7 fixed, 注意顺序 */
}
</style>
注意:
*+html 对IE7的HACK 必须保证HTML顶部有如下声明:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
二、万能 float 闭合
关于 clear float 的原理可参见 [How To Clear Floats Without Structural Markup]
将以下代码加入Global CSS 中,给需要闭合的div加上 class="clearfix" 即可,屡试不爽.
<style>
/* Clear Fix */
.clearfix:after
{
content:".";
display:block;
height:0;
clear:both;
visibility:hidden;
}
.clearfix
{
display:inline-block;
}
/* Hide from IE Mac */
.clearfix {display:block;}
/* End hide from IE Mac */
/* end of clearfix */
</style>
三、其他兼容技巧
1, FF下给 div 设置 padding 后会导致 width 和 height 增加, 但IE不会.(可用!important解决)
2, 居中问题.
1).垂直居中.将 line-height 设置为 当前 div 相同的高度, 再通过 vertical-align: middle.( 注意内容不要换行.)
2).水平居中. margin: 0 auto;(当然不是万能)
3, 若需给 a 标签内内容加上 样式, 需要设置 display: block;(常见于导航标签)
4, FF 和 IE 对 BOX 理解的差异导致相差 2px 的还有设为 float的div在ie下 margin加倍等问题.
5, ul 标签在 FF 下面默认有 list-style 和 padding . 最好事先声明, 以避免不必要的麻烦. (常见于导航标签和内容列表)
6, 作为外部 wrapper 的 div 不要定死高度, 最好还加上 overflow: hidden.以达到高度自适应.
7, 关于手形光标. cursor: pointer. 而hand 只适用于 IE.
2 css布局中的居中问题
主要的样式定义如下:
body {TEXT-ALIGN: center;}
#center { MARGIN-RIGHT: auto; MARGIN-LEFT: auto; }
说明:
首先在父级元素定义TEXT-ALIGN: center;这个的意思就是在父级元素内的内容居中;对于IE这样设定就已经可以了。
但在mozilla中不能居中。解决办法就是在子元素定义时候设定时再加上“MARGIN-RIGHT: auto;MARGIN-LEFT: auto; ”
需要说明的是,如果你想用这个方法使整个页面要居中,建议不要套在一个DIV里,你可以依次拆出多个div,
只要在每个拆出的div里定义MARGIN-RIGHT: auto;MARGIN-LEFT: auto; 就可以了。
3 盒模型不同解释
#box{ width:600px; //for ie6.0- w\idth:500px; //for ff+ie6.0}
#box{ width:600px!important //for ff width:600px; //for ff+ie6.0 width /**/:500px; //for ie6.0-}
4 浮动ie产生的双倍距离
#box{ float:left; width:100px; margin:0 0 0 100px; //这种情况之下IE会产生200px的距离 display:inline; //使浮动忽略}
这里细说一下block,inline两个元素,Block元素的特点是:总是在新行上开始,高度,宽度,行高,边距都可以控制(块元素);Inline元素的特点是:和其他元素在同一行上,...不可控制(内嵌元素);
#box{ display:block; //可以为内嵌元素模拟为块元素 display:inline; //实现同一行排列的的效果 diplay:table;
IE不认得min-这个定义,但实际上它把正常的width和height当作有min的情况来使。这样问题就大了,如果只用宽度和高度,
正常的浏览器里这两个值就不会变,如果只用min-width和min-height的话,IE下面根本等于没有设置宽度和高度。
比如要设置背景图片,这个宽度是比较重要的。要解决这个问题,可以这样:
#box{ width: 80px; height: 35px;}html>body #box{ width: auto; height: auto; min-width: 80px; min-height: 35px;}
6 页面的最小宽度
min-width是个非常方便的CSS命令,它可以指定元素最小也不能小于某个宽度,这样就能保证排版一直正确。但IE不认得这个,
而它实际上把width当做最小宽度来使。为了让这一命令在IE上也能用,可以把一个<div> 放到 <body> 标签下,然后为div指定一个类:
然后CSS这样设计:
#container{ min-width: 600px; width:expression(document.body.clientWidth < 600? "600px": "auto" );}
第一个min-width是正常的;但第2行的width使用了Javascript,这只有IE才认得,这也会让你的HTML文档不太正规。它实际上通过Javascript的判断来实现最小宽度。
7 清除浮动
.hackbox{ display:table; //将对象作为块元素级的表格显示}或者.hackbox{ clear:both;}
或者加入:after(伪对象),设置在对象后发生的内容,通常和content配合使用,IE不支持此伪对象,非Ie 浏览器支持,
所 以并不影响到IE/WIN浏览器。这种的最麻烦的......#box:after{ content: "."; display: block; height: 0; clear: both; visibility: hidden;}
8 DIV浮动IE文本产生3象素的bug
左边对象浮动,右边采用外补丁的左边距来定位,右边对象内的文本会离左边有3px的间距.
#box{ float:left; width:800px;}#left{ float:left; width:50%;}#right{ width:50%;}*html #left{ margin-right:-3px; //这句是关键}
HTML代码<div id="box"> <div id="left"></div> <div id="right"></div></div>
9 属性选择器(这个不能算是兼容,是隐藏css的一个bug)
p[id]{}div[id]{}
这个对于IE6.0和IE6.0以下的版本都隐藏,FF和OPera作用
属性选择器和子选择器还是有区别的,子选择器的范围从形式来说缩小了,属性选择器的范围比较大,如p[id]中,所有p标签中有id的都是同样式的.
10 IE捉迷藏的问题
当div应用复杂的时候每个栏中又有一些链接,DIV等这个时候容易发生捉迷藏的问题。
有些内容显示不出来,当鼠标选择这个区域是发现内容确实在页面。
解决办法:对#layout使用line-height属性 或者给#layout使用固定高和宽。页面结构尽量简单。
11 高度不适应
高度不适应是当内层对象的高度发生变化时外层高度不能自动进行调节,特别是当内层对象使用
margin 或paddign 时。
例:
<div id="box">
<p>p对象中的内容</p>
</div>
CSS:#box {background-color:#eee; }
#box p {margin-top: 20px;margin-bottom: 20px; text-align:center; }
解决方法:在P对象上下各加2个空的div对象CSS代码:.1{height:0px;overflow:hidden;}或者为DIV加上border属性。
/*IE与Firefox的CSS兼容大全*/
1.DOCTYPE 影响 CSS 处理
2.FF: div 设置 margin-left, margin-right 为 auto 时已经居中, IE 不行
3.FF: body 设置 text-align 时, div 需要设置 margin: auto(主要是 margin-left,margin-right) 方可居中
4.FF: 设置 padding 后, div 会增加 height 和 width, 但 IE 不会, 故需要用 !important 多设一个 height 和 width
5.FF: 支持 !important, IE 则忽略, 可用 !important 为 FF 特别设置样式
6.div 的垂直居中问题: vertical-align:middle; 将行距增加到和整个DIV一样高 line-height:200px; 然后插入文字,就垂直居中了。缺点是要控制内容不要换行
7.cursor: pointer 可以同时在 IE FF 中显示游标手指状, hand 仅 IE 可以
8.FF: 链接加边框和背景色,需设置 display: block, 同时设置 float: left 保证不换行。参照 menubar, 给 a 和 menubar 设置高度是为了避免底边显示错位, 若不设 height, 可以在 menubar 中插入一个空格。
9.在mozilla firefox和IE中的BOX模型解释不一致导致相差2px解决方法:
div{margin:30px!important;margin:28px;}
注意这两个margin的顺序一定不能写反,据阿捷的说法!important这个属性IE不能识别,但别的浏览器可以识别。所以在IE下其实解释成这样:
div{maring:30px;margin:28px}
重复定义的话按照最后一个来执行,所以不可以只写margin:XXpx!important;
10.IE5 和IE6的BOX解释不一致
IE5下
div{width:300px;margin:0 10px 0 10px;}
div的宽度会被解释为300px-10px(右填充)-10px(左填充)最终div的宽度为280px,而在IE6和其他浏览器上宽度则是以300px+10px(右填充)+10px(左填充)=320px来计算的。这时我们可以做如下修改
div{width:300px!important;width /**/:340px;margin:0 10px 0 10px}
关于这个/**/是什么我也不太明白,只知道IE5和firefox都支持但IE6不支持,如果有人理解的话,请告诉我一声,谢了!:)
11.ul标签在Mozilla中默认是有padding值的,而在IE中只有margin有值所以先定义
ul{margin:0;padding:0;}
就能解决大部分问题
注意事项:
1、float的div一定要闭合。
例如:(其中floatA、floatB的属性已经设置为float:left;)
<#div id="floatA" ></#div>
<#div id="floatB" ></#div>
<#div id="NOTfloatC" ></#div>
这里的NOTfloatC并不希望继续平移,而是希望往下排。
这段代码在IE中毫无问题,问题出在FF。原因是NOTfloatC并非float标签,必须将float标签闭合。
在
<#div class="floatB"></#div>
<#div class="NOTfloatC"></#div>
之间加上
<#div class="clear"></#div>
这个div一定要注意声明位置,一定要放在最恰当的地方,而且必须与两个具有float属性的div同级,之间不能存在嵌套关系,否则会产生异常。
并且将clear这种样式定义为为如下即可:
.clear{
clear:both;}
此外,为了让高度能自动适应,要在wrapper里面加上overflow:hidden;
当包含float的box的时候,高度自动适应在IE下无效,这时候应该触发IE的layout私有属性(万恶的IE啊!)用zoom:1;可以做到,这样就达到了兼容。
例如某一个wrapper如下定义:
.colwrapper{
overflow:hidden;
zoom:1;
margin:5px auto;}
2、margin加倍的问题。
设置为float的div在ie下设置的margin会加倍。这是一个ie6都存在的bug。
解决方案是在这个div里面加上display:inline;
例如:
<#div id="imfloat"></#div>
相应的css为
#IamFloat{
float:left;
margin:5px;/*IE下理解为10px*/
display:inline;/*IE下再理解为5px*/}
3、关于容器的包涵关系
很多时候,尤其是容器内有平行布局,例如两、三个float的div时,宽度很容易出现问题。在IE中,外层的宽度会被内层更宽的div挤破。一定要用Photoshop或者Firework量取像素级的精度。
4、关于高度的问题
如果是动态地添加内容,高度最好不要定义。浏览器可以自动伸缩,然而如果是静态的内容,高度最好定好。(似乎有时候不会自动往下撑开,不知道具体怎么回事)
5、最狠的手段 - !important;
如果实在没有办法解决一些细节问题,可以用这个方法.FF对于"!important"会自动优先解析,然而IE则会忽略.如下
.tabd1{
background:url(/res/images/up/tab1.gif) no-repeat 0px 0px !important; /*Style for FF*/
background:url(/res/images/up/tab1.gif) no-repeat 1px 0px; /* Style for IE */}
CSS兼容性2
发布于:2014-7-30 18:51 作者:admin 浏览:2115 分类:CSS!important 可被FireFox和IE7识别
* 可被IE6、IE7识别
_ 可被IE6识别
*+ 可被IE7识别
2.IE专用的条件注释
<!--其他浏览器 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css.css" />
<!--[if IE 7]>
<!-- 适合于IE7 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="ie7.css" />
<![endif]-->
<!--[if lte IE 6]>
<!-- 适合于IE6及一下 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="ie.css" />
<![endif]-->
3. 几个浏览器对实际像素的解释
IE/Opera:对象的实际宽度 = (margin-left) + width + (margin-right)
Firefox/Mozilla:对象的实际宽度= (margin-left) + (border-left-width) + (padding- left) + width + (padding-right) + (border-right-width) + (margin-right)
4.鼠标手势问题:
FireFox的cursor属性不支持hand,但是支持pointer,IE两个都支持;所以为了兼容都用pointer
5.统一加px单位
FireFox中设置HTML标签的Style属性时,所有位置、宽高和尺寸值必须后跟px,IE也支持此写法,因此统一加px单位。如 Obj.Style.Height = imgObj.Style.Height + ‘px’;
6.FireFox无法解析简写的padding属性设置,
如padding 5px 4px 3px 1px;必须改为 padding-top:5px; padding-right:4px; padding-bottom:3px; padding-left:1px0;
7.消除ul、ol等列表的缩进,
样式应写成:list-style:none;margin:0px;padding:0px;其中margin属性对IE有效,padding属性对FireFox有效
8.CSS控制透 明:
IE:filter:progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.Alpha(style=0,opacity=60); FireFox:opacity:0.6;
9.CSS控制圆角:IE:不支持圆角;
FireFox: -moz-border-radius:4px;或
-moz-border-radius-topleft:4px;
-moz-border-radius-topright:4px;
-moz-border-radius-bottomleft:4px;
-moz-border-radius- bottomright:4px;
10.CSS双线凹凸边框:
IE:border:2px outset;
FireFox:
-moz-border-top-colors: #d4d0c8 white;
-moz-border-left-colors: #d4d0c8 white;
-moz-border-right-colors:#404040 #808080;
-moz-border-bottom-colors:#404040 #808080;
11.自定义光标样式文件和滚动条颜色风格
IE支持CSS方法cursor:url()自定义光标样式文件和滚动条颜色风格;FireFox对以上两者均不支持
12.Select控件永远处于最上层的bug
IE有Select控件永远处于最上层的bug,且所有CSS对Select控件都不起作用
13.Label标签
IE支持Form中的Label标签,包括图片和文字内容;FireFox不支持包含图片的Label,点击图片不能让标记 label for 的Radio或CheckBox产生效果
14.FireFox中的TextArea不支持onScroll事件
15.FireFox不支持display的inline和block
16.FireFox对Div设置margin-left, margin-right为auto时已经居中, IE中不行
17.FireFox对Body设置text-align时, Div需要设置margin: auto(主要是margin-left margin-right) 方可居中
18.对超链接的CSS样式设置最好遵从这样的顺序:L-V-H-A。即
<style type="text/css">
<!--
a:link {}
a:visited {}
a:hover {}
a:active {}
-->
</style>
这样可以避免一些访问过后的超链接就不具备hover和active样式了
19.IE中设置长段落自动换行在CSS中设置word-wrap:break-word。
20.在子容器加了浮动属性后,该容器将不能自动撑开
解决方法:在标签结束后下一个标签中加上一个清除浮动的CSS clear:both;
22.IE6下图片下方会有空隙
解决办法:为img加上display:block或设置vertical-align 属性为vertical-align:top | bottom |middle |text-bottom
23.IE6下两个层中间有空隙
解决办法:设置右侧div也同样浮动float:left或者相对IE6定义 margin-right:-3px;
24.LI中内容超过长度后以省略号的显示方法
<style type="text/css">
<!--
li {
width:200px;
white-space:nowrap;
text-overflow:ellipsis;
-o-text-overflow:ellipsis;
overflow: hidden;
}
-->
</style>
25.将元素的高度和行高设为相同值,即可垂直居中文本
<style type="text/css">
<!--
div {
height:30px;
line-height:30px;
}
-->
</style>
26.对齐文本与文本输入框,须在CSS中增加vertical-align:middle;属性设置
<style type="text/css">
<!--
… …
vertical-align:middle;
}
-->
</style>
27.支持WEB标准的浏览器设置了固定高度值就不会像IE6那样被撑开,但是又想设置固定高度又想能够被撑开呢?解决办法是去掉height属性而设置min-height,为了兼容不支持min-height的IE6可以这样定义:
{
height:auto!important;
height:200px;
min-height:200px;
}
28.web标准中IE无法设置滚动条颜色
解决办法:在CSS中对body的设置改为对html的
<style type="text/css">
<!--
html {
scrollbar-face-color:#f6f6f6;
scrollbar-highlight-color:#fff;
scrollbar-shadow-color:#eeeeee;
scrollbar-3dlight-color:#eeeeee;
scrollbar-arrow-color:#000;
scrollbar-track-color:#fff;
scrollbar-darkshadow-color:#fff;
}
-->
</style>
29.IE6由于默认行高问题无法定义1px左右高度的容器,
解决办法:在CSS中对容器设置如:overflow:hidden | zoom:0.08 | line-height:1px
30.给Flash设置透明属性可使层显示在Flash之上
<param name="wmode" value="transparent" /> <!-- 解决IE上的问题 //>
<embed wmode="transparent" …… > <!-- 解决FireFox上的问题 //>
31.FireFox设置Padding属性后会相应的增加Width和Height属性值,IE不会
解决办法:用!important方法多定义一套Height和Width
32.FireFox对div与div之间的空格是忽略的,但IE是处理的;因此尽量在两个相连的div之间不要有空格和回车,否则可能会造成不同浏览器之间格式不正确,比如著名的3px偏差;而且原因很难查明
33.形如如下格式
<div id="parent">
<div id="content"> </div>
</div>
当Content内容多时,即使parent设置了高度100%或auto,在不同浏览器下还是不能完好的自动伸展;解决办法在层的最下方产生一个高度为1的空格,代码如下
<div id="parent">
<div id="content"> </div>
<div style="font: 0px/0px sans-serif;clear: both;display: block"> </div>
</div>
34.IE和FireFox对字体small的尺寸解释不同,FireFox为13px,IE中为16px
35.IE和FireFox对空格的尺寸解释不同,FireFox为4px,IE中为8px
36.在netvibes的CSS看到一个片断
.transparent{
filter:alpha(opacity=12);
-moz-opacity:0.12;
opacity:0.12;
background-color:#000;
}
filter:alpha(opacity=12); 支持IE
-moz-opacity:0.12; 支持FF
opacity:0.12; css 3标准
CSS兼容性1
发布于:2014-7-30 18:35 作者:admin 浏览:2145 分类:CSS1、DOCTYPE 影响 CSS 处理
2、div padding 的height 和 width问题
FF: 设置 padding 后, div 会增加 height 和 width, 但 IE 不会, 故需要用 !important 多设一个 height 和 width
3、!important 问题
FF: 支持 !important, IE 则忽略, 可用 !important 为 FF 特别设置样式
4、垂直居中问题
div 的垂直居中问题: vertical-align:middle; 将行距增加到和整个DIV一样高 line-height:200px; 然后插入文字,就垂直居中了。缺点是要控制内容不要换行
5、IE中的BOX模型解释不一致导致相差2px解决方法
在mozilla firefox和IE中的BOX模型解释不一致导致相差2px解决方法:
div{margin:30px!important;margin:28px;}
注意这两个margin的顺序一定不能写反,!important这个属性IE不能识别,但别的浏览器可以识别。所以在IE下其实解释成这样:
div{maring:30px;margin:28px}
重复定义的话按照最后一个来执行,所以不可以只写margin:30px!important;
6、ul和ol列表缩进问题
消除ul、ol等列表的缩进时,样式应写成:list-style:none;margin:0px;padding:0px;
其中margin属性对IE有效,padding属性对FireFox有效。
[注]经验证,在IE中,设置margin:0px可以去除列表的上下左右缩进、空白以及列表编号或圆点,设置padding对样式没有影响;在 Firefox 中,设置margin:0px仅仅可以去除上下的空白,设置padding:0px后仅仅可以去掉左右缩进,还必须设置list- style:none才 能去除列表编号或圆点。也就是说,在IE中仅仅设置margin:0px即可达到最终效果,而在Firefox中必须同时设置margin:0px、 padding:0px以及list-style:none三项才能达到最终效果。
7、CSS透明问题
IE:filter:progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.Alpha(style=0,opacity=60)。
FF:opacity:0.6。
[注] 最好两个都写,并将opacity属性放在下面。
8、CSS圆角问题
IE:ie7以下版本不支持圆角。
FF: -moz-border-radius:4px,或者-moz-border-radius-topleft:4px;-moz- border- radius-topright:4px;-moz-border-radius-bottomleft:4px;-moz- border- radius- bottomright:4px;。
[注] 圆角问题是CSS中的经典问题,建议使用JQuery框架集来设置圆角,让这些复杂的问题留给别人去想吧。不过jQuery的圆角只看到支持整个区域的圆角,没有支持边框的圆角,不过这个边框的圆角可以通过一些简单的手段来实现,下次有机会介绍下。
9、cursor:hand VS cursor:pointer
问题说明:firefox不支持hand,但ie支持pointer ,两者都是手形指示。
解决方法:统一使用pointer。
10、字体大小定义不同
对字体大小small的定义不同,Firefox中为13px,而IE中为16px,差别挺大。
解决方法:使用指定的字体大小如14px。
并列排列的多个元素(图片或者链接)的div和div之间,代码中的空格和回车在firefox中都会被忽略,而IE中却默认显示为空格(约3px)。
11、CSS双线凹凸边框
IE:border:2px outset;。
FF: -moz-border-top-colors: #d4d0c8 white;-moz-border-left-colors: #d4d0c8 white;-moz-border-right-colors:#404040 #808080;-moz-border-bottom-colors:#404040 #808080;
12、IE的双边距bug
设置为float的div在ie下设置的margin会加倍。这是一个ie6都存在的bug。
解决方案:在这个div里面加上display:inline;
例如:
<#div id=”imfloat”>
相应的css为
以下为引用的内容:
#IamFloat{
float:left;
margin:5px;/*IE下理解为10px*/
display:inline;/*IE下再理解为5px*/
}
#IamFloat{
float:left;
margin:5px;/*IE下理解为10px*/
display:inline;/*IE下再理解为5px*/
}
关于CSS中的问题实在太多了,甚至同样的CSS定义在不同的页面标准中的显示效果都是不一样的。一个合乎发展的建议是,页面采用标准XHTML标准编写,较少使用table,CSS定义尽量依照标准DOM,同时兼顾IE、Firefox、Opera等主流浏览器。很多情况下,FF和 Opera的CSS解释标准更贴近CSS标准,也更具有规范性。
13、IE选择符空格BUG 一个空格也可以使样式失效。
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "//www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="//www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
<!--
p{font-size:12px;}
p:first-letter{font-size:300%}
-->
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>对于世界而言,你是一个人;但是对于某个人,你是他的整个世界。纵然伤心,也不要愁眉不展,因为你不知是谁会爱上你的笑容。</p>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "//www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="//www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
<!--
p{font-size:12px;}
p:first-letter{font-size:300%}
-->
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>对于世界而言,你是一个人;但是对于某个人,你是他的整个世界。纵然伤心,也不要愁眉不展,因为你不知是谁会爱上你的笑容。</p>
</body>
</html>
这段代码对<p>的首字符样式定义在IE6上看是没有效果的(IE7没测试),而在p:first-letter和{font-size:300%}加上空格,也就是p:first-letter {font-size:300%}后,显示就正常了。但是同样的代码,在FireFox下看是正常的。按道理说,p:first-letter{font-size:300%}的写法是没错的。那么问题出在哪里呢?答案是伪类中的连字符”-”。IE有个BUG,在处理伪类时,如果伪类的名称中带有连字符”-”,伪类名称后面就得跟一个空格,不然样式的定义就无效。而在FF中,加不加空格都可以正常处理。
Android数据库SQLite的使用示例
发布于:2014-7-22 9:55 作者:admin 浏览:2975 分类:Android
package com.android.tutor;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
public class BooksDB extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private final static String DATABASE_NAME = "BOOKS.db";
private final static int DATABASE_VERSION = 1;
private final static String TABLE_NAME = "books_table";
public final static String BOOK_ID = "book_id";
public final static String BOOK_NAME = "book_name";
public final static String BOOK_AUTHOR = "book_author";
public BooksDB(Context context) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
super(context, DATABASE_NAME, null, DATABASE_VERSION);
}
//创建table
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
String sql = "CREATE TABLE " + TABLE_NAME + " (" + BOOK_ID
+ " INTEGER primary key autoincrement, " + BOOK_NAME + " text, "+ BOOK_AUTHOR +" text);";
db.execSQL(sql);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
String sql = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS " + TABLE_NAME;
db.execSQL(sql);
onCreate(db);
}
public Cursor select() {
SQLiteDatabase db = this.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db
.query(TABLE_NAME, null, null, null, null, null, null);
return cursor;
}
//增加操作
public long insert(String bookname,String author)
{
SQLiteDatabase db = this.getWritableDatabase();
/* ContentValues */
ContentValues cv = new ContentValues();
cv.put(BOOK_NAME, bookname);
cv.put(BOOK_AUTHOR, author);
long row = db.insert(TABLE_NAME, null, cv);
return row;
}
//删除操作
public void delete(int id)
{
SQLiteDatabase db = this.getWritableDatabase();
String where = BOOK_ID + " = ?";
String[] whereValue ={ Integer.toString(id) };
db.delete(TABLE_NAME, where, whereValue);
}
//修改操作
public void update(int id, String bookname,String author)
{
SQLiteDatabase db = this.getWritableDatabase();
String where = BOOK_ID + " = ?";
String[] whereValue = { Integer.toString(id) };
ContentValues cv = new ContentValues();
cv.put(BOOK_NAME, bookname);
cv.put(BOOK_AUTHOR, author);
db.update(TABLE_NAME, cv, where, whereValue);
}
}
第三步:修改main.xml布局如下,由两个EditText和一个ListView组成,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <EditText android:id="@+id/bookname" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > </EditText> <EditText android:id="@+id/author" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > </EditText> <ListView android:id="@+id/bookslist" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > </ListView> </LinearLayout>第四步:修改SQLiteDatabaseDemo.java代码如下:
package com.android.tutor;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class SQLiteDatabaseDemo extends Activity implements AdapterView.OnItemClickListener {
private BooksDB mBooksDB;
private Cursor mCursor;
private EditText BookName;
private EditText BookAuthor;
private ListView BooksList;
private int BOOK_ID = 0;
protected final static int MENU_ADD = Menu.FIRST;
protected final static int MENU_DELETE = Menu.FIRST + 1;
protected final static int MENU_UPDATE = Menu.FIRST + 2;
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
setUpViews();
}
public void setUpViews(){
mBooksDB = new BooksDB(this);
mCursor = mBooksDB.select();
BookName = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.bookname);
BookAuthor = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.author);
BooksList = (ListView)findViewById(R.id.bookslist);
BooksList.setAdapter(new BooksListAdapter(this, mCursor));
BooksList.setOnItemClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
super.onCreateOptionsMenu(menu);
menu.add(Menu.NONE, MENU_ADD, 0, "ADD");
menu.add(Menu.NONE, MENU_DELETE, 0, "DELETE");
menu.add(Menu.NONE, MENU_DELETE, 0, "UPDATE");
return true;
}
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item)
{
super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
switch (item.getItemId())
{
case MENU_ADD:
add();
break;
case MENU_DELETE:
delete();
break;
case MENU_UPDATE:
update();
break;
}
return true;
}
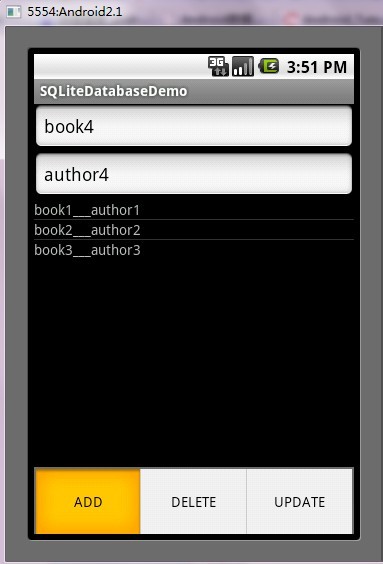
public void add(){
String bookname = BookName.getText().toString();
String author = BookAuthor.getText().toString();
//书名和作者都不能为空,或者退出
if (bookname.equals("") || author.equals("")){
return;
}
mBooksDB.insert(bookname, author);
mCursor.requery();
BooksList.invalidateViews();
BookName.setText("");
BookAuthor.setText("");
Toast.makeText(this, "Add Successed!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
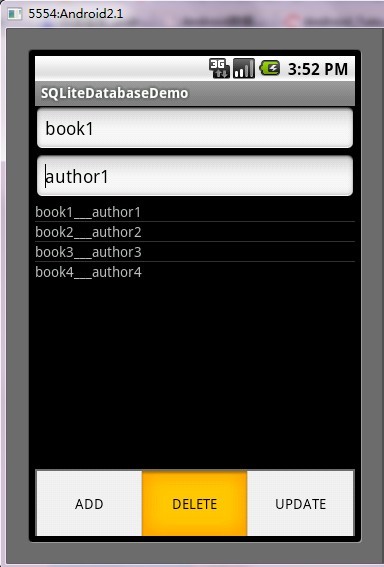
public void delete(){
if (BOOK_ID == 0) {
return;
}
mBooksDB.delete(BOOK_ID);
mCursor.requery();
BooksList.invalidateViews();
BookName.setText("");
BookAuthor.setText("");
Toast.makeText(this, "Delete Successed!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
public void update(){
String bookname = BookName.getText().toString();
String author = BookAuthor.getText().toString();
//书名和作者都不能为空,或者退出
if (bookname.equals("") || author.equals("")){
return;
}
mBooksDB.update(BOOK_ID, bookname, author);
mCursor.requery();
BooksList.invalidateViews();
BookName.setText("");
BookAuthor.setText("");
Toast.makeText(this, "Update Successed!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
mCursor.moveToPosition(position);
BOOK_ID = mCursor.getInt(0);
BookName.setText(mCursor.getString(1));
BookAuthor.setText(mCursor.getString(2));
}
public class BooksListAdapter extends BaseAdapter{
private Context mContext;
private Cursor mCursor;
public BooksListAdapter(Context context,Cursor cursor) {
mContext = context;
mCursor = cursor;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return mCursor.getCount();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return null;
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
TextView mTextView = new TextView(mContext);
mCursor.moveToPosition(position);
mTextView.setText(mCursor.getString(1) + "___" + mCursor.getString(2));
return mTextView;
}
}
}
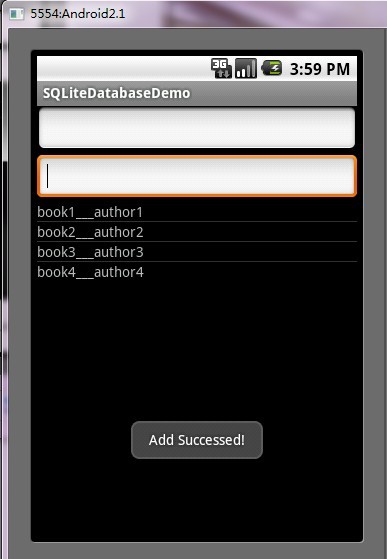
第五步:运行程序效果如下:
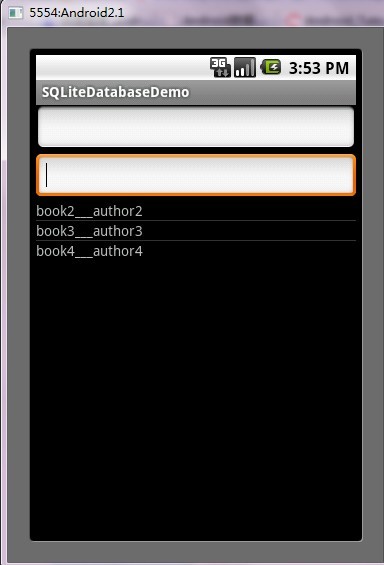
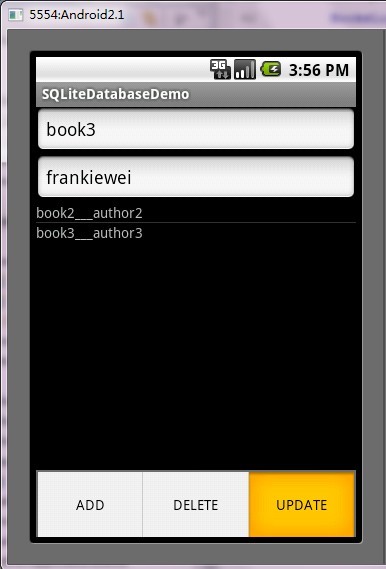
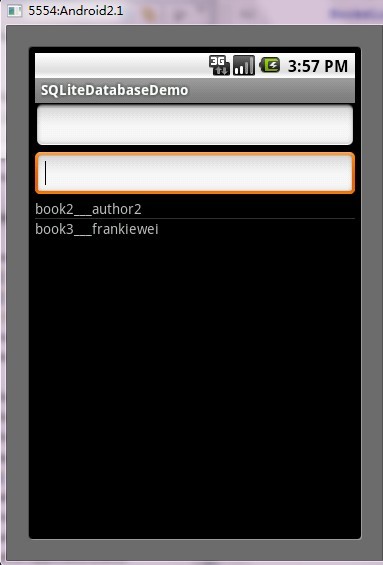
ANDROID开发之SQLite详解
发布于:2014-7-22 9:47 作者:admin 浏览:2381 分类:AndroidSQLite简介
Google为Andriod的较大的数据处理提供了SQLite,他在数据存储、管理、维护等各方面都相当出色,功能也非常的强大。SQLite具备下列特点:
1.轻量级
使用 SQLite 只需要带一个动态库,就可以享受它的全部功能,而且那个动态库的尺寸想当小。
2.独立性
SQLite 数据库的核心引擎不需要依赖第三方软件,也不需要所谓的“安装”。
3.隔离性
SQLite 数据库中所有的信息(比如表、视图、触发器等)都包含在一个文件夹内,方便管理和维护。
4.跨平台
SQLite 目前支持大部分操作系统,不至电脑操作系统更在众多的手机系统也是能够运行,比如:Android。
5.多语言接口
SQLite 数据库支持多语言编程接口。
6.安全性
SQLite 数据库通过数据库级上的独占性和共享锁来实现独立事务处理。这意味着多个进程可以在同一时间从同一数据库读取数据,但只能有一个可以写入数据。
Android中的SQLite使用
首先创建数据库类
|
public class DatabaseHelperextends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private static final String DB_NAME ="mydata.db";//数据库名称
private static final int version =1;//数据库版本
public DatabaseHelper(Context context) {
super(context, DB_NAME,null, version);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
String sql ="create table user(username varchar(20) not null , password varchar(60) not null );";
db.execSQL(sql);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db,int oldVersion,int newVersion) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
|
SQLiteOpenHelper类介绍
SQLiteOpenHelper是SQLiteDatabase的一个帮助类,用来管理数据库的创建和版本的更新。一般是建立一个类继承它,并实现它的onCreate和onUpgrade方法。
| 方法名 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| SQLiteOpenHelper(Context context,String name,SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory,int version) | 构造方法,一般是传递一个要创建的数据库名称那么参数 |
| onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) | 创建数据库时调用 |
| onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db,int oldVersion , int newVersion) | 版本更新时调用 |
| getReadableDatabase() | 创建或打开一个只读数据库 |
| getWritableDatabase() | 创建或打开一个读写数据库 |
下面来介绍调用的方法
创建数据库
这里特别的地方是通过调用了SQLiteOpenHelper类的getReadableDatabase()方法来实现创建一个数据库的
|
1
2
3
|
DatabaseHelper database =new DatabaseHelper(this);//这段代码放到Activity类中才用this
SQLiteDatabase db =null;
db = database.getReadalbeDatabase();
|
SQLiteDatabase类为我们提供了很多种方法,而较常用的方法如下
| (返回值)方法名 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| (int) delete(String table,String whereClause,String[] whereArgs) | 删除数据行的便捷方法 |
| (long) insert(String table,String nullColumnHack,ContentValues values) | 添加数据行的便捷方法 |
| (int) update(String table, ContentValues values, String whereClause, String[] whereArgs) | 更新数据行的便捷方法 |
| (void) execSQL(String sql) | 执行一个SQL语句,可以是一个select或其他的sql语句 |
| (void) close() | 关闭数据库 |
| (Cursor) query(String table, String[] columns, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String groupBy, String having, String orderBy, String limit) | 查询指定的数据表返回一个带游标的数据集 |
| (Cursor) rawQuery(String sql, String[] selectionArgs) | 运行一个预置的SQL语句,返回带游标的数据集(与上面的语句最大的区别就是防止SQL注入) |
数据的添删改查分别可以通过2种途径来实现
数据的添加
1.使用insert方法
|
1
2
3
|
ContentValues cv =new ContentValues();//实例化一个ContentValues用来装载待插入的数据cv.put("username","Jack Johnson");//添加用户名
cv.put("password","iLovePopMusic");//添加密码
db.insert("user",null,cv);//执行插入操作
|
2.使用execSQL方式来实现
|
1
2
|
String sql = "insert into user(username,password) values ('Jack Johnson','iLovePopMuisc');//插入操作的SQL语句
db.execSQL(sql);//执行SQL语句
|
数据的删除
同样有2种方式可以实现
|
1
2
3
|
String whereClause ="username=?";//删除的条件
String[] whereArgs = {"Jack Johnson"};//删除的条件参数
db.delete("user",whereClause,whereArgs);//执行删除
|
使用execSQL方式的实现
|
1
2
|
String sql ="delete from user where username='Jack Johnson'";//删除操作的SQL语句
db.execSQL(sql);//执行删除操作
|
数据修改
同上,仍是2种方式
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
ContentValues cv =new ContentValues();//实例化ContentValues
cv.put("password","iHatePopMusic");//添加要更改的字段及内容
String whereClause ="username=?";//修改条件
String[] whereArgs = {"Jack Johnson"};//修改条件的参数
db.update("user",cv,whereClause,whereArgs);//执行修改
|
使用execSQL方式的实现
|
1
2
|
String sql ="update [user] set password = 'iHatePopMusic' where username='Jack Johnson'";//修改的SQL语句
db.execSQL(sql);//执行修改
|
数据查询
数据查询相对前面几种方法就复杂一些了,因为查询会带有很多条件
通过query实现查询的
public Cursor query(String table, String[] columns, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String groupBy, String having, String orderBy, String limit)
各参数说明:
- table:表名称
- colums:列名称数组
- selection:条件子句,相当于where
- selectionArgs:条件语句的参数数组
- groupBy:分组
- having:分组条件
- orderBy:排序类
- limit:分页查询的限制
- Cursor:返回值,相当于结果集ResultSet
针对游标(Cursor)也提供了不少方法
| 方法名称 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| getCount() | 总记录条数 |
| isFirst() | 判断是否第一条记录 |
| isLast() | 判断是否最后一条记录 |
| moveToFirst() | 移动到第一条记录 |
| moveToLast() | 移动到最后一条记录 |
| move(int offset) | 移动到指定的记录 |
| moveToNext() | 移动到吓一条记录 |
| moveToPrevious() | 移动到上一条记录 |
| getColumnIndex(String columnName) | 获得指定列索引的int类型值 |
实现代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
Cursor c = db.query("user",null,null,null,null,null,null);//查询并获得游标
if(c.moveToFirst()){//判断游标是否为空
for(int i=0;i<c.getCount();i++){
c.move(i);//移动到指定记录
String username = c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("username");
String password = c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("password"));
}
}
|
通过rawQuery实现的带参数查询
|
1
2
3
4
|
Cursor c = db.rawQuery("select * from user where username=?",new Stirng[]{"Jack Johnson"});
if(cursor.moveToFirst()) {
String password = c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("password"));
}
|
Android中SQLite应用详解
发布于:2014-7-22 9:35 作者:admin 浏览:2463 分类:Android现在的主流移动设备像Android、iPhone等都使用SQLite作为复杂数据的存储引擎,在我们为移动设备开发应用程序时,也许就要使用到SQLite来存储我们大量的数据,所以我们就需要掌握移动设备上的SQLite开发技巧。对于Android平台来说,系统内置了丰富的API来供开发人员操作SQLite,我们可以轻松的完成对数据的存取。
下面就向大家介绍一下SQLite常用的操作方法,为了方便,我将代码写在了Activity的onCreate中:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//打开或创建test.db数据库
SQLiteDatabase db = openOrCreateDatabase("test.db", Context.MODE_PRIVATE, null);
db.execSQL("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS person");
//创建person表
db.execSQL("CREATE TABLE person (_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, name VARCHAR, age SMALLINT)");
Person person = new Person();
person.name = "john";
person.age = 30;
//插入数据
db.execSQL("INSERT INTO person VALUES (NULL, ?, ?)", new Object[]{person.name, person.age});
person.name = "david";
person.age = 33;
//ContentValues以键值对的形式存放数据
ContentValues cv = new ContentValues();
cv.put("name", person.name);
cv.put("age", person.age);
//插入ContentValues中的数据
db.insert("person", null, cv);
cv = new ContentValues();
cv.put("age", 35);
//更新数据
db.update("person", cv, "name = ?", new String[]{"john"});
Cursor c = db.rawQuery("SELECT * FROM person WHERE age >= ?", new String[]{"33"});
while (c.moveToNext()) {
int _id = c.getInt(c.getColumnIndex("_id"));
String name = c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("name"));
int age = c.getInt(c.getColumnIndex("age"));
Log.i("db", "_id=>" + _id + ", name=>" + name + ", age=>" + age);
}
c.close();
//删除数据
db.delete("person", "age < ?", new String[]{"35"});
//关闭当前数据库
db.close();
//删除test.db数据库
// deleteDatabase("test.db");
}
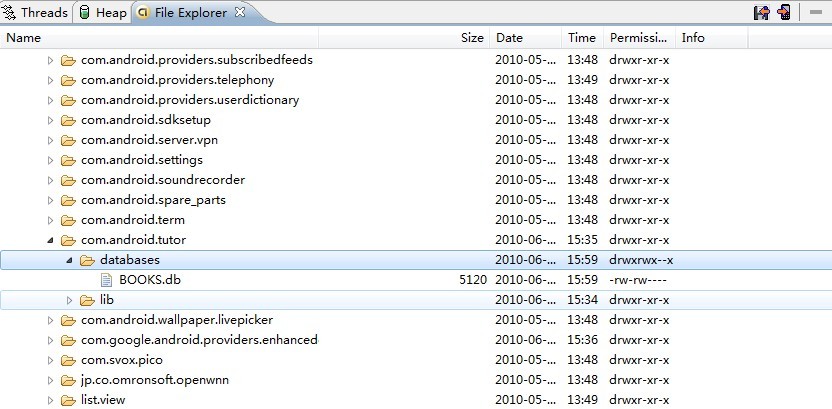
在执行完上面的代码后,系统就会在/data/data/[PACKAGE_NAME]/databases目录下生成一个“test.db”的数据库文件,如图:
上面的代码中基本上囊括了大部分的数据库操作;对于添加、更新和删除来说,我们都可以使用
- db.executeSQL(String sql);
- db.executeSQL(String sql, Object[] bindArgs);//sql语句中使用占位符,然后第二个参数是实际的参数集
- db.insert(String table, String nullColumnHack, ContentValues values);
- db.update(String table, Contentvalues values, String whereClause, String whereArgs);
- db.delete(String table, String whereClause, String whereArgs);
下面来说说查询操作。查询操作相对于上面的几种操作要复杂些,因为我们经常要面对着各种各样的查询条件,所以系统也考虑到这种复杂性,为我们提供了较为丰富的查询形式:
- db.rawQuery(String sql, String[] selectionArgs);
- db.query(String table, String[] columns, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String groupBy, String having, String orderBy);
- db.query(String table, String[] columns, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String groupBy, String having, String orderBy, String limit);
- db.query(String distinct, String table, String[] columns, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String groupBy, String having, String orderBy, String limit);
最后,他们同时返回一个Cursor对象,代表数据集的游标,有点类似于JavaSE中的ResultSet。
下面是Cursor对象的常用方法
- c.move(int offset); //以当前位置为参考,移动到指定行
- c.moveToFirst(); //移动到第一行
- c.moveToLast(); //移动到最后一行
- c.moveToPosition(int position); //移动到指定行
- c.moveToPrevious(); //移动到前一行
- c.moveToNext(); //移动到下一行
- c.isFirst(); //是否指向第一条
- c.isLast(); //是否指向最后一条
- c.isBeforeFirst(); //是否指向第一条之前
- c.isAfterLast(); //是否指向最后一条之后
- c.isNull(int columnIndex); //指定列是否为空(列基数为0)
- c.isClosed(); //游标是否已关闭
- c.getCount(); //总数据项数
- c.getPosition(); //返回当前游标所指向的行数
- c.getColumnIndex(String columnName);//返回某列名对应的列索引值
- c.getString(int columnIndex); //返回当前行指定列的值
在上面的代码示例中,已经用到了这几个常用方法中的一些,关于更多的信息,大家可以参考官方文档中的说明。
最后当我们完成了对数据库的操作后,记得调用SQLiteDatabase的close()方法释放数据库连接,否则容易出现SQLiteException。
上面就是SQLite的基本应用,但在实际开发中,为了能够更好的管理和维护数据库,我们会封装一个继承自SQLiteOpenHelper类的数据库操作类,然后以这个类为基础,再封装我们的业务逻辑方法。
下面,我们就以一个实例来讲解具体的用法,我们新建一个名为db的项目,结构如下:

其中DBHelper继承了SQLiteOpenHelper,作为维护和管理数据库的基类,DBManager是建立在DBHelper之上,封装了常用的业务方法,Person是我们的person表对应的JavaBean,MainActivity就是我们显示的界面。
下面我们先来看一下DBHelper:
- package com.scott.db;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
- import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
- public class DBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
- private static final String DATABASE_NAME = "test.db";
- private static final int DATABASE_VERSION = 1;
- public DBHelper(Context context) {
- //CursorFactory设置为null,使用默认值
- super(context, DATABASE_NAME, null, DATABASE_VERSION);
- }
- //数据库第一次被创建时onCreate会被调用
- @Override
- public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
- db.execSQL("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS person" +
- "(_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, name VARCHAR, age INTEGER, info TEXT)");
- }
- //如果DATABASE_VERSION值被改为2,系统发现现有数据库版本不同,即会调用onUpgrade
- @Override
- public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
- db.execSQL("ALTER TABLE person ADD COLUMN other STRING");
- }
- }
为了方便我们面向对象的使用数据,我们建一个Person类,对应person表中的字段,如下:
- package com.scott.db;
- public class Person {
- public int _id;
- public String name;
- public int age;
- public String info;
- public Person() {
- }
- public Person(String name, int age, String info) {
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- this.info = info;
- }
- }
- package com.scott.db;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.List;
- import android.content.ContentValues;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.database.Cursor;
- import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
- public class DBManager {
- private DBHelper helper;
- private SQLiteDatabase db;
- public DBManager(Context context) {
- helper = new DBHelper(context);
- //因为getWritableDatabase内部调用了mContext.openOrCreateDatabase(mName, 0, mFactory);
- //所以要确保context已初始化,我们可以把实例化DBManager的步骤放在Activity的onCreate里
- db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
- }
- /**
- * add persons
- * @param persons
- */
- public void add(List<Person> persons) {
- db.beginTransaction(); //开始事务
- try {
- for (Person person : persons) {
- db.execSQL("INSERT INTO person VALUES(null, ?, ?, ?)", new Object[]{person.name, person.age, person.info});
- }
- db.setTransactionSuccessful(); //设置事务成功完成
- } finally {
- db.endTransaction(); //结束事务
- }
- }
- /**
- * update person's age
- * @param person
- */
- public void updateAge(Person person) {
- ContentValues cv = new ContentValues();
- cv.put("age", person.age);
- db.update("person", cv, "name = ?", new String[]{person.name});
- }
- /**
- * delete old person
- * @param person
- */
- public void deleteOldPerson(Person person) {
- db.delete("person", "age >= ?", new String[]{String.valueOf(person.age)});
- }
- /**
- * query all persons, return list
- * @return List<Person>
- */
- public List<Person> query() {
- ArrayList<Person> persons = new ArrayList<Person>();
- Cursor c = queryTheCursor();
- while (c.moveToNext()) {
- Person person = new Person();
- person._id = c.getInt(c.getColumnIndex("_id"));
- person.name = c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("name"));
- person.age = c.getInt(c.getColumnIndex("age"));
- person.info = c.getString(c.getColumnIndex("info"));
- persons.add(person);
- }
- c.close();
- return persons;
- }
- /**
- * query all persons, return cursor
- * @return Cursor
- */
- public Cursor queryTheCursor() {
- Cursor c = db.rawQuery("SELECT * FROM person", null);
- return c;
- }
- /**
- * close database
- */
- public void closeDB() {
- db.close();
- }
- }
我们获取数据库实例时使用了getWritableDatabase()方法,也许朋友们会有疑问,在getWritableDatabase()和getReadableDatabase()中,你为什么选择前者作为整个应用的数据库实例呢?在这里我想和大家着重分析一下这一点。
我们来看一下SQLiteOpenHelper中的getReadableDatabase()方法:
- public synchronized SQLiteDatabase getReadableDatabase() {
- if (mDatabase != null && mDatabase.isOpen()) {
- // 如果发现mDatabase不为空并且已经打开则直接返回
- return mDatabase;
- }
- if (mIsInitializing) {
- // 如果正在初始化则抛出异常
- throw new IllegalStateException("getReadableDatabase called recursively");
- }
- // 开始实例化数据库mDatabase
- try {
- // 注意这里是调用了getWritableDatabase()方法
- return getWritableDatabase();
- } catch (SQLiteException e) {
- if (mName == null)
- throw e; // Can't open a temp database read-only!
- Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't open " + mName + " for writing (will try read-only):", e);
- }
- // 如果无法以可读写模式打开数据库 则以只读方式打开
- SQLiteDatabase db = null;
- try {
- mIsInitializing = true;
- String path = mContext.getDatabasePath(mName).getPath();// 获取数据库路径
- // 以只读方式打开数据库
- db = SQLiteDatabase.openDatabase(path, mFactory, SQLiteDatabase.OPEN_READONLY);
- if (db.getVersion() != mNewVersion) {
- throw new SQLiteException("Can't upgrade read-only database from version " + db.getVersion() + " to "
- + mNewVersion + ": " + path);
- }
- onOpen(db);
- Log.w(TAG, "Opened " + mName + " in read-only mode");
- mDatabase = db;// 为mDatabase指定新打开的数据库
- return mDatabase;// 返回打开的数据库
- } finally {
- mIsInitializing = false;
- if (db != null && db != mDatabase)
- db.close();
- }
- }
- public synchronized SQLiteDatabase getWritableDatabase() {
- if (mDatabase != null && mDatabase.isOpen() && !mDatabase.isReadOnly()) {
- // 如果mDatabase不为空已打开并且不是只读模式 则返回该实例
- return mDatabase;
- }
- if (mIsInitializing) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("getWritableDatabase called recursively");
- }
- // If we have a read-only database open, someone could be using it
- // (though they shouldn't), which would cause a lock to be held on
- // the file, and our attempts to open the database read-write would
- // fail waiting for the file lock. To prevent that, we acquire the
- // lock on the read-only database, which shuts out other users.
- boolean success = false;
- SQLiteDatabase db = null;
- // 如果mDatabase不为空则加锁 阻止其他的操作
- if (mDatabase != null)
- mDatabase.lock();
- try {
- mIsInitializing = true;
- if (mName == null) {
- db = SQLiteDatabase.create(null);
- } else {
- // 打开或创建数据库
- db = mContext.openOrCreateDatabase(mName, 0, mFactory);
- }
- // 获取数据库版本(如果刚创建的数据库,版本为0)
- int version = db.getVersion();
- // 比较版本(我们代码中的版本mNewVersion为1)
- if (version != mNewVersion) {
- db.beginTransaction();// 开始事务
- try {
- if (version == 0) {
- // 执行我们的onCreate方法
- onCreate(db);
- } else {
- // 如果我们应用升级了mNewVersion为2,而原版本为1则执行onUpgrade方法
- onUpgrade(db, version, mNewVersion);
- }
- db.setVersion(mNewVersion);// 设置最新版本
- db.setTransactionSuccessful();// 设置事务成功
- } finally {
- db.endTransaction();// 结束事务
- }
- }
- onOpen(db);
- success = true;
- return db;// 返回可读写模式的数据库实例
- } finally {
- mIsInitializing = false;
- if (success) {
- // 打开成功
- if (mDatabase != null) {
- // 如果mDatabase有值则先关闭
- try {
- mDatabase.close();
- } catch (Exception e) {
- }
- mDatabase.unlock();// 解锁
- }
- mDatabase = db;// 赋值给mDatabase
- } else {
- // 打开失败的情况:解锁、关闭
- if (mDatabase != null)
- mDatabase.unlock();
- if (db != null)
- db.close();
- }
- }
- }
看完上面的过程之后,大家或许就清楚了许多,如果不是在遇到磁盘空间已满等情况,getReadableDatabase()一般都会返回和getWritableDatabase()一样的数据库实例,所以我们在DBManager构造方法中使用getWritableDatabase()获取整个应用所使用的数据库实例是可行的。当然如果你真的担心这种情况会发生,那么你可以先用getWritableDatabase()获取数据实例,如果遇到异常,再试图用getReadableDatabase()获取实例,当然这个时候你获取的实例只能读不能写了。
最后,让我们看一下如何使用这些数据操作方法来显示数据,下面是MainActivity.java的布局文件和代码:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent">
- <Button
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="add"
- android:onClick="add"/>
- <Button
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="update"
- android:onClick="update"/>
- <Button
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="delete"
- android:onClick="delete"/>
- <Button
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="query"
- android:onClick="query"/>
- <Button
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="queryTheCursor"
- android:onClick="queryTheCursor"/>
- <ListView
- android:id="@+id/listView"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
- </LinearLayout>
- package com.scott.db;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.List;
- import java.util.Map;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.database.Cursor;
- import android.database.CursorWrapper;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.widget.ListView;
- import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
- import android.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
- private DBManager mgr;
- private ListView listView;
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.main);
- listView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listView);
- //初始化DBManager
- mgr = new DBManager(this);
- }
- @Override
- protected void onDestroy() {
- super.onDestroy();
- //应用的最后一个Activity关闭时应释放DB
- mgr.closeDB();
- }
- public void add(View view) {
- ArrayList<Person> persons = new ArrayList<Person>();
- Person person1 = new Person("Ella", 22, "lively girl");
- Person person2 = new Person("Jenny", 22, "beautiful girl");
- Person person3 = new Person("Jessica", 23, "sexy girl");
- Person person4 = new Person("Kelly", 23, "hot baby");
- Person person5 = new Person("Jane", 25, "a pretty woman");
- persons.add(person1);
- persons.add(person2);
- persons.add(person3);
- persons.add(person4);
- persons.add(person5);
- mgr.add(persons);
- }
- public void update(View view) {
- Person person = new Person();
- person.name = "Jane";
- person.age = 30;
- mgr.updateAge(person);
- }
- public void delete(View view) {
- Person person = new Person();
- person.age = 30;
- mgr.deleteOldPerson(person);
- }
- public void query(View view) {
- List<Person> persons = mgr.query();
- ArrayList<Map<String, String>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
- for (Person person : persons) {
- HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
- map.put("name", person.name);
- map.put("info", person.age + " years old, " + person.info);
- list.add(map);
- }
- SimpleAdapter adapter = new SimpleAdapter(this, list, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_2,
- new String[]{"name", "info"}, new int[]{android.R.id.text1, android.R.id.text2});
- listView.setAdapter(adapter);
- }
- public void queryTheCursor(View view) {
- Cursor c = mgr.queryTheCursor();
- startManagingCursor(c); //托付给activity根据自己的生命周期去管理Cursor的生命周期
- CursorWrapper cursorWrapper = new CursorWrapper(c) {
- @Override
- public String getString(int columnIndex) {
- //将简介前加上年龄
- if (getColumnName(columnIndex).equals("info")) {
- int age = getInt(getColumnIndex("age"));
- return age + " years old, " + super.getString(columnIndex);
- }
- return super.getString(columnIndex);
- }
- };
- //确保查询结果中有"_id"列
- SimpleCursorAdapter adapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_2,
- cursorWrapper, new String[]{"name", "info"}, new int[]{android.R.id.text1, android.R.id.text2});
- ListView listView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listView);
- listView.setAdapter(adapter);
- }
- }
如果手动去管理Cursor的话会非常的麻烦,还有一定的风险,处理不当的话运行期间就会出现异常,幸好Activity为我们提供了startManagingCursor(Cursor cursor)方法,它会根据Activity的生命周期去管理当前的Cursor对象,下面是该方法的说明:
- /**
- * This method allows the activity to take care of managing the given
- * {@link Cursor}'s lifecycle for you based on the activity's lifecycle.
- * That is, when the activity is stopped it will automatically call
- * {@link Cursor#deactivate} on the given Cursor, and when it is later restarted
- * it will call {@link Cursor#requery} for you. When the activity is
- * destroyed, all managed Cursors will be closed automatically.
- *
- * @param c The Cursor to be managed.
- *
- * @see #managedQuery(android.net.Uri , String[], String, String[], String)
- * @see #stopManagingCursor
- */
如何包装Cursor:我们会使用到CursorWrapper对象去包装我们的Cursor对象,实现我们需要的数据转换工作,这个CursorWrapper实际上是实现了Cursor接口。我们查询获取到的Cursor其实是Cursor的引用,而系统实际返回给我们的必然是Cursor接口的一个实现类的对象实例,我们用CursorWrapper包装这个实例,然后再使用SimpleCursorAdapter将结果显示到列表上。
Cursor结果集需要注意些什么:一个最需要注意的是,在我们的结果集中必须要包含一个“_id”的列,否则SimpleCursorAdapter就会翻脸不认人,为什么一定要这样呢?因为这源于SQLite的规范,主键以“_id”为标准。解决办法有三:第一,建表时根据规范去做;第二,查询时用别名,例如:SELECT id AS _id FROM person;第三,在CursorWrapper里做文章:
- CursorWrapper cursorWrapper = new CursorWrapper(c) {
- @Override
- public int getColumnIndexOrThrow(String columnName) throws IllegalArgumentException {
- if (columnName.equals("_id")) {
- return super.getColumnIndex("id");
- }
- return super.getColumnIndexOrThrow(columnName);
- }
- };

android 参数含义
发布于:2014-7-21 13:38 作者:admin 浏览:2583android:layout_height 设置组件的高度
android:id 给组件定义一个id值,供后期使用
android:background 设置组件的背景颜色或背景图片
android:text 设置组件的显示文字
android:textColor 设置组件的显示文字的颜色
android:layout_below 组件在参考组件的下面
android:alignTop 同指定组件的顶平行
android:maxLength="6" 限制输入字数
android:digits='012356789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'限制输入数字和大写小写字母
1. 开发更简单,执行速度高效。 2. 输入法默认会根据情况变动,比如说设置为numeric后输入法会自动仅显示数字,不会出现Qwerty中的字母。
下面我们通过EditText的layout xml文件中的相关属性来实现:
1. 密码框属性 android:password='true' 这条可以让EditText显示的内容自动为 星号,输入时内容会在1秒内变成*字样。
2. 纯数字 android:numeric='true' 这条可以让输入法自动变为数字输入键盘,同时仅允许0-9的数字输入
3. 仅允许 android:capitalize='cwj1987' 这样仅允许接受输入cwj1987,一般用于密码验证
下面是一些扩展的风格属性
android:editable='false' 设置EditText不可编辑
android:singleLine='true' 强制输入的内容在单行
android:ellipsize='end' 自动隐藏尾部溢出数据,一般用于文字内容过长一行无法全部显示时。
android:autoLink
设置是否当文本为URL链接/email/电话号码/map时,文本显示为可点击的链接。可选值(none/web/email/phone/map/all)
android:autoText
如果设置,将自动执行输入值的拼写纠正。此处无效果,在显示输入法并输入的时候起作用。
android:bufferType
指定getText()方式取得的文本类别。选项editable 类似于StringBuilder可追加字符,
也就是说getText后可调用append方法设置文本内容。spannable 则可在给定的字符区域使用样式,参见这里1、这里2。
android:capitalize
设置英文字母大写类型。此处无效果,需要弹出输入法才能看得到,参见EditText此属性说明。
android:cursorVisible
设定光标为显示/隐藏,默认显示。
android:digits
设置允许输入哪些字符。如“1234567890.+-*/%\n()”
android:drawableBottom
在text的下方输出一个drawable,如图片。如果指定一个颜色的话会把text的背景设为该颜色,并且同时和background使用时覆盖后者。
android:drawableLeft
在text的左边输出一个drawable,如图片。
android:drawablePadding
设置text与drawable(图片)的间隔,与drawableLeft、drawableRight、drawableTop、drawableBottom一起使用,可设置为负数,单独使用没有效果。
android:drawableRight
在text的右边输出一个drawable,如图片。
android:drawableTop
在text的正上方输出一个drawable,如图片。
android:editable
设置是否可编辑。这里无效果,参见EditView。
android:editorExtras
设置文本的额外的输入数据。在EditView再讨论。
android:ellipsize
设置当文字过长时,该控件该如何显示。有如下值设置:”start”—–省略号显示在开头;”end”——省略号显示在结尾;”middle”—-省略号显示在中间;”marquee” ——以跑马灯的方式显示(动画横向移动)
android:freezesText
设置保存文本的内容以及光标的位置。参见:这里。
android:gravity
设置文本位置,如设置成“center”,文本将居中显示。
android:hint
Text为空时显示的文字提示信息,可通过textColorHint设置提示信息的颜色。此属性在EditView中使用,但是这里也可以用。
android:imeOptions
附加功能,设置右下角IME动作与编辑框相关的动作,如actionDone右下角将显示一个“完成”,而不设置默认是一个回车符号。这个在EditText中再详细说明,此处无用。
android:imeActionId
设置IME动作ID。在EditText再做说明,可以先看这篇帖子:这里。
android:imeActionLabel
设置IME动作标签。在EditText再做说明。
android:includeFontPadding
设置文本是否包含顶部和底部额外空白,默认为true。
android:inputMethod
为文本指定输入法,需要完全限定名(完整的包名)。例如:com.google.android.inputmethod.pinyin,但是这里报错找不到。
android:inputType
设置文本的类型,用于帮助输入法显示合适的键盘类型。在EditText中再详细说明,这里无效果。
android:linksClickable
设置链接是否点击连接,即使设置了autoLink。
android:marqueeRepeatLimit
在ellipsize指定marquee的情况下,设置重复滚动的次数,当设置为marquee_forever时表示无限次。
android:ems
设置TextView的宽度为N个字符的宽度。这里测试为一个汉字字符宽度,如图:
android:maxEms
设置TextView的宽度为最长为N个字符的宽度。与ems同时使用时覆盖ems选项。
android:minEms
设置TextView的宽度为最短为N个字符的宽度。与ems同时使用时覆盖ems选项。
android:maxLength
限制显示的文本长度,超出部分不显示。
android:lines
设置文本的行数,设置两行就显示两行,即使第二行没有数据。
android:maxLines
设置文本的最大显示行数,与width或者layout_width结合使用,超出部分自动换行,超出行数将不显示。
android:minLines
设置文本的最小行数,与lines类似。
android:lineSpacingExtra
设置行间距。
android:lineSpacingMultiplier
设置行间距的倍数。如”1.2”
android:numeric
如果被设置,该TextView有一个数字输入法。此处无用,设置后唯一效果是TextView有点击效果,此属性在EditText将详细说明。
android:password
以小点”.”显示文本
android:phoneNumber
设置为电话号码的输入方式。
android:privateImeOptions
设置输入法选项,此处无用,在EditText将进一步讨论。
android:scrollHorizontally
设置文本超出TextView的宽度的情况下,是否出现横拉条。
android:selectAllOnFocus
如果文本是可选择的,让他获取焦点而不是将光标移动为文本的开始位置或者末尾位置。EditText中设置后无效果。
android:shadowColor
指定文本阴影的颜色,需要与shadowRadius一起使用。效果:
android:shadowDx
设置阴影横向坐标开始位置。
android:shadowDy
设置阴影纵向坐标开始位置。
android:shadowRadius
设置阴影的半径。设置为0.1就变成字体的颜色了,一般设置为3.0的效果比较好。
android:singleLine
设置单行显示。如果和layout_width一起使用,当文本不能全部显示时,后面用“…”来表示。如android:text="test_ singleLine " android:singleLine="true" android:layout_width="20dp"将只显示“t…”。如果不设置singleLine或者设置为false,文本将自动换行
android:text
设置显示文本.
android:textAppearance
设置文字外观。如“?android:attr/textAppearanceLargeInverse
”这里引用的是系统自带的一个外观,?表示系统是否有这种外观,否则使用默认的外观。可设置的值如下:textAppearanceButton/textAppearanceInverse/textAppearanceLarge/textAppearanceLargeInverse/textAppearanceMedium/textAppearanceMediumInverse/textAppearanceSmall/textAppearanceSmallInverse
android:textColor
设置文本颜色
android:textColorHighlight
被选中文字的底色,默认为蓝色
android:textColorHint
设置提示信息文字的颜色,默认为灰色。与hint一起使用。
android:textColorLink
文字链接的颜色.
android:textScaleX
设置文字之间间隔,默认为1.0f。分别设置0.5f/1.0f/1.5f/2.0f效果如下:
android:textSize
设置文字大小,推荐度量单位”sp”,如”15sp”
android:textStyle
设置字形[bold(粗体) 0, italic(斜体) 1, bolditalic(又粗又斜) 2] 可以设置一个或多个,用“|”隔开
android:typeface
设置文本字体,必须是以下常量值之一:normal 0, sans 1, serif 2, monospace(等宽字体) 3]
android:height
设置文本区域的高度,支持度量单位:px(像素)/dp/sp/in/mm(毫米)
android:maxHeight
设置文本区域的最大高度
android:minHeight
设置文本区域的最小高度
android:width
设置文本区域的宽度,支持度量单位:px(像素)/dp/sp/in/mm(毫米),与layout_width的区别看这里。
android:maxWidth
设置文本区域的最大宽度
android:minWidth
设置文本区域的最小宽度
Android Notification通知详解
发布于:2014-7-18 9:38 作者:admin 浏览:2387 分类:Android根据activity的生命周期,在activity不显示时,会执行onStop函数(比如按下home键),所以你在onStop函数(按退出键除外)里面把notification放在通知栏里,再此显示时,把notification从通知栏里去掉。或者,只要程序在运行就一直显示通知栏图标。
下面对Notification类中的一些常量,字段,方法简单介绍一下:
常量:
DEFAULT_ALL 使用所有默认值,比如声音,震动,闪屏等等
DEFAULT_LIGHTS 使用默认闪光提示
DEFAULT_SOUNDS 使用默认提示声音
DEFAULT_VIBRATE 使用默认手机震动
【说明】:加入手机震动,一定要在manifest.xml中加入权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.VIBRATE" />
以上的效果常量可以叠加,即通过
notification.defaults =DEFAULT_SOUND|DEFAULT_VIBRATE;
notification.defaults |= DEFAULT_SOUND (最好在真机上测试,震动效果模拟器上没有)
//设置flag位
FLAG_AUTO_CANCEL 该通知能被状态栏的清除按钮给清除掉
FLAG_NO_CLEAR 该通知能被状态栏的清除按钮给清除掉
FLAG_ONGOING_EVENT 通知放置在正在运行
FLAG_INSISTENT 是否一直进行,比如音乐一直播放,知道用户响应
常用字段:
contentIntent 设置PendingIntent对象,点击时发送该Intent
defaults 添加默认效果
flags 设置flag位,例如FLAG_NO_CLEAR等
icon 设置图标
sound 设置声音
tickerText 显示在状态栏中的文字
when 发送此通知的时间戳
NotificationManager常用方法介绍:
public void cancelAll() 移除所有通知(只是针对当前Context下的Notification)
public void cancel(int id) 移除标记为id的通知 (只是针对当前Context下的所有Notification)
public void notify(String tag ,int id, Notification notification) 将通知加入状态栏,标签为tag,标记为id
public void notify(int id, Notification notification) 将通知加入状态栏,标记为id
package com.ljq.activity;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Notification;
import android.app.NotificationManager;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
clearNotification();
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
showNotification();
super.onStop();
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
clearNotification();
super.onStart();
}
/**
* 在状态栏显示通知
*/
private void showNotification(){
// 创建一个NotificationManager的引用
NotificationManager notificationManager = (NotificationManager)
this.getSystemService(android.content.Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
// 定义Notification的各种属性
Notification notification =new Notification(R.drawable.icon,
"督导系统", System.currentTimeMillis());
//FLAG_AUTO_CANCEL 该通知能被状态栏的清除按钮给清除掉
//FLAG_NO_CLEAR 该通知不能被状态栏的清除按钮给清除掉
//FLAG_ONGOING_EVENT 通知放置在正在运行
//FLAG_INSISTENT 是否一直进行,比如音乐一直播放,知道用户响应
notification.flags |= Notification.FLAG_ONGOING_EVENT; // 将此通知放到通知栏的"Ongoing"即"正在运行"组中
notification.flags |= Notification.FLAG_NO_CLEAR; // 表明在点击了通知栏中的"清除通知"后,此通知不清除,经常与FLAG_ONGOING_EVENT一起使用
notification.flags |= Notification.FLAG_SHOW_LIGHTS;
//DEFAULT_ALL 使用所有默认值,比如声音,震动,闪屏等等
//DEFAULT_LIGHTS 使用默认闪光提示
//DEFAULT_SOUNDS 使用默认提示声音
//DEFAULT_VIBRATE 使用默认手机震动,需加上<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.VIBRATE" />权限
notification.defaults = Notification.DEFAULT_LIGHTS;
//叠加效果常量
//notification.defaults=Notification.DEFAULT_LIGHTS|Notification.DEFAULT_SOUND;
notification.ledARGB = Color.BLUE;
notification.ledOnMS =5000; //闪光时间,毫秒
// 设置通知的事件消息
CharSequence contentTitle ="督导系统标题"; // 通知栏标题
CharSequence contentText ="督导系统内容"; // 通知栏内容
Intent notificationIntent =new Intent(MainActivity.this, MainActivity.class); // 点击该通知后要跳转的Activity
PendingIntent contentItent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, notificationIntent, 0);
notification.setLatestEventInfo(this, contentTitle, contentText, contentItent);
// 把Notification传递给NotificationManager
notificationManager.notify(0, notification);
}
?
//删除通知
private void clearNotification(){
// 启动后删除之前我们定义的通知
NotificationManager notificationManager = (NotificationManager) this
.getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
notificationManager.cancel(0);
}
}android intent和intent action大全
发布于:2014-7-18 8:30 作者:admin 浏览:5754 分类:Android(1)用Action跳转
Intent i = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW,uri);手机的Intent分发过程中,会根据http://www.google.com 的scheme判断出数据类型type 。手机的Brower则能匹配它,在Brower的Manifest.xml中的IntenFilter中 首先有ACTION_VIEW Action,也能处理http:的type,
intent.setClass(context, targetActivy.class);
//或者直接用 Intent intent = new Intent(context, targetActivity.class);
★intent大全:
1.从google搜索内容
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_WEB_SEARCH);
intent.putExtra(SearchManager.QUERY,"searchString")
startActivity(intent);
2.浏览网页
Uri uri = Uri.parse("http://www.google.com");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW,uri);
startActivity(it);
3.显示地图
Uri uri = Uri.parse("geo:38.899533,-77.036476");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.Action_VIEW,uri);
startActivity(it);
4.路径规划
Uri uri = Uri.parse("http://maps.google.com/maps?f=dsaddr=startLat%20startLng&daddr=endLat%20endLng&hl=en");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW,URI);
startActivity(it);
5.拨打电话
Uri uri = Uri.parse("tel:xxxxxx");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_DIAL, uri);
startActivity(it);
6.调用发短信的程序
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
it.putExtra("sms_body", "The SMS text");
it.setType("vnd.android-dir/mms-sms");
startActivity(it);
7.发送短信
Uri uri = Uri.parse("smsto:0800000123");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SENDTO, uri);
it.putExtra("sms_body", "The SMS text");
startActivity(it);
String body="this is sms demo";
Intent mmsintent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SENDTO, Uri.fromParts("smsto", number, null));
mmsintent.putExtra(Messaging.KEY_ACTION_SENDTO_MESSAGE_BODY, body);
mmsintent.putExtra(Messaging.KEY_ACTION_SENDTO_COMPOSE_MODE, true);
mmsintent.putExtra(Messaging.KEY_ACTION_SENDTO_EXIT_ON_SENT, true);
startActivity(mmsintent);
8.发送彩信
Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://media/external/images/media/23");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
it.putExtra("sms_body", "some text");
it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_STREAM, uri);
it.setType("image/png");
startActivity(it);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("file://");
sb.append(fd.getAbsoluteFile());
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SENDTO, Uri.fromParts("mmsto", number, null));
// Below extra datas are all optional.
intent.putExtra(Messaging.KEY_ACTION_SENDTO_MESSAGE_SUBJECT, subject);
intent.putExtra(Messaging.KEY_ACTION_SENDTO_MESSAGE_BODY, body);
intent.putExtra(Messaging.KEY_ACTION_SENDTO_CONTENT_URI, sb.toString());
intent.putExtra(Messaging.KEY_ACTION_SENDTO_COMPOSE_MODE, composeMode);
intent.putExtra(Messaging.KEY_ACTION_SENDTO_EXIT_ON_SENT, exitOnSent);
startActivity(intent);
9.发送Email
Uri uri = Uri.parse("mailto:xxx@abc.com");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SENDTO, uri);
startActivity(it);
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_EMAIL, "me@abc.com");
it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_TEXT, "The email body text");
it.setType("text/plain");
startActivity(Intent.createChooser(it, "Choose Email Client"));
Intent it=new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
String[] tos={"me@abc.com"};
String[] ccs={"you@abc.com"};
it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_EMAIL, tos);
it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CC, ccs);
it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_TEXT, "The email body text");
it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_SUBJECT, "The email subject text");
it.setType("message/rfc822");
startActivity(Intent.createChooser(it, "Choose Email Client"));
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_SUBJECT, "The email subject text");
it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_STREAM, "file:///sdcard/mysong.mp3");
sendIntent.setType("audio/mp3");
startActivity(Intent.createChooser(it, "Choose Email Client"));
10.播放多媒体
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
Uri uri = Uri.parse("file:///sdcard/song.mp3");
it.setDataAndType(uri, "audio/mp3");
startActivity(it);
Uri uri = Uri.withAppendedPath(MediaStore.Audio.Media.INTERNAL_CONTENT_URI, "1");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(it);
11.uninstall apk
Uri uri = Uri.fromParts("package", strPackageName, null);
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_DELETE, uri);
startActivity(it);
12.install apk
Uri installUri = Uri.fromParts("package", "xxx", null);
returnIt = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED, installUri);
13. 打开照相机
<1>Intent i = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CAMERA_BUTTON, null);
this.sendBroadcast(i);
<2>long dateTaken = System.currentTimeMillis();
String name = createName(dateTaken) + ".jpg";
fileName = folder + name;
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(Images.Media.TITLE, fileName);
values.put("_data", fileName);
values.put(Images.Media.PICASA_ID, fileName);
values.put(Images.Media.DISPLAY_NAME, fileName);
values.put(Images.Media.DESCRIPTION, fileName);
values.put(Images.ImageColumns.BUCKET_DISPLAY_NAME, fileName);
Uri photoUri = getContentResolver().insert(
MediaStore.Images.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI, values);
Intent inttPhoto = new Intent(MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE);
inttPhoto.putExtra(MediaStore.EXTRA_OUTPUT, photoUri);
startActivityForResult(inttPhoto, 10);
14.从gallery选取图片
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setType("image/*");
i.setAction(Intent.ACTION_GET_CONTENT);
startActivityForResult(i, 11);
15. 打开录音机
Intent mi = new Intent(Media.RECORD_SOUND_ACTION);
startActivity(mi);
16.显示应用详细列表
Uri uri = Uri.parse("market://details?id=app_id");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(it);
//where app_id is the application ID, find the ID
//by clicking on your application on Market home
//page, and notice the ID from the address bar
刚才找app id未果,结果发现用package name也可以
Uri uri = Uri.parse("market://details?id=<packagename>");
这个简单多了
17寻找应用
Uri uri = Uri.parse("market://search?q=pname:pkg_name");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(it);
//where pkg_name is the full package path for an application
18打开联系人列表
<1>
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setAction(Intent.ACTION_GET_CONTENT);
i.setType("vnd.android.cursor.item/phone");
startActivityForResult(i, REQUEST_TEXT);
<2>
Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://contacts/people");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_PICK, uri);
startActivityForResult(it, REQUEST_TEXT);
19 打开另一程序
Intent i = new Intent();
ComponentName cn = new ComponentName("com.yellowbook.android2",
"com.yellowbook.android2.AndroidSearch");
i.setComponent(cn);
i.setAction("android.intent.action.MAIN");
startActivityForResult(i, RESULT_OK);
Intent it = newIntent(Intent.ACTION_INSERT_OR_EDIT);
it.setType("vnd.android.cursor.item/contact");
//it.setType(Contacts.CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE);
it.putExtra("name","myName");
it.putExtra(android.provider.Contacts.Intents.Insert.COMPANY, "organization");
it.putExtra(android.provider.Contacts.Intents.Insert.EMAIL,"email");
it.putExtra(android.provider.Contacts.Intents.Insert.PHONE,"homePhone");
it.putExtra(android.provider.Contacts.Intents.Insert.SECONDARY_PHONE,
"mobilePhone");
it.putExtra( android.provider.Contacts.Intents.Insert.TERTIARY_PHONE,
"workPhone");
it.putExtra(android.provider.Contacts.Intents.Insert.JOB_TITLE,"title");
startActivity(it);
21.调用系统编辑添加联系人(全有效):
Intent intent = newIntent(Intent.ACTION_INSERT_OR_EDIT);
intent.setType(People.CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE);
intent.putExtra(Contacts.Intents.Insert.NAME, "My Name");
intent.putExtra(Contacts.Intents.Insert.PHONE, "+1234567890");
intent.putExtra(Contacts.Intents.Insert.PHONE_TYPE,Contacts.PhonesColumns.TYPE_MOBILE);
intent.putExtra(Contacts.Intents.Insert.EMAIL, "com@com.com");
intent.putExtra(Contacts.Intents.Insert.EMAIL_TYPE,
startActivity(intent);
★intent action大全:
- android.intent.action.ALL_APPS
- android.intent.action.ANSWER
- android.intent.action.ATTACH_DATA
- android.intent.action.BUG_REPORT
- android.intent.action.CALL
- android.intent.action.CALL_BUTTON
- android.intent.action.CHOOSER
- android.intent.action.CREATE_LIVE_FOLDER
- android.intent.action.CREATE_SHORTCUT
- android.intent.action.DELETE
- android.intent.action.DIAL
- android.intent.action.EDIT
- android.intent.action.GET_CONTENT
- android.intent.action.INSERT
- android.intent.action.INSERT_OR_EDIT
- android.intent.action.MAIN
- android.intent.action.MEDIA_SEARCH
- android.intent.action.PICK
- android.intent.action.PICK_ACTIVITY
- android.intent.action.RINGTONE_PICKER
- android.intent.action.RUN
- android.intent.action.SEARCH
- android.intent.action.SEARCH_LONG_PRESS
- android.intent.action.SEND
- android.intent.action.SENDTO
- android.intent.action.SET_WALLPAPER
- android.intent.action.SYNC
- android.intent.action.SYSTEM_TUTORIAL
- android.intent.action.VIEW
- android.intent.action.VOICE_COMMAND
- android.intent.action.WEB_SEARCH
- android.net.wifi.PICK_WIFI_NETWORK
- android.settings.AIRPLANE_MODE_SETTINGS
- android.settings.APN_SETTINGS
- android.settings.APPLICATION_DEVELOPMENT_SETTINGS
- android.settings.APPLICATION_SETTINGS
- android.settings.BLUETOOTH_SETTINGS
- android.settings.DATA_ROAMING_SETTINGS
- android.settings.DATE_SETTINGS
- android.settings.DISPLAY_SETTINGS
- android.settings.INPUT_METHOD_SETTINGS
- android.settings.INTERNAL_STORAGE_SETTINGS
- android.settings.LOCALE_SETTINGS
- android.settings.LOCATION_SOURCE_SETTINGS
- android.settings.MANAGE_APPLICATIONS_SETTINGS
- android.settings.MEMORY_CARD_SETTINGS
- android.settings.NETWORK_OPERATOR_SETTINGS
- android.settings.QUICK_LAUNCH_SETTINGS
- android.settings.SECURITY_SETTINGS
- android.settings.SETTINGS
- android.settings.SOUND_SETTINGS
- android.settings.SYNC_SETTINGS
- android.settings.USER_DICTIONARY_SETTINGS
- android.settings.WIFI_IP_SETTINGS
- android.settings.WIFI_SETTINGS
- android.settings.WIRELESS_SETTINGS
附录:
|
String |
"android.intent.action.ADD_SHORTCUT" |
动作:在系统中添加一个快捷方式。. |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.ALL_APPS" |
动作:列举所有可用的应用。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.ANSWER" |
动作:处理拨入的电话。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.BUG_REPORT" |
动作:显示 activity 报告错误。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.CALL" |
动作:拨打电话,被呼叫的联系人在数据中指定。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.CLEAR_CREDENTIALS" |
动作:清除登陆凭证 (credential)。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.VIEW" |
动作:和 VIEW_ACTION 相同,是在数据上执行的标准动作。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.DELETE" |
动作:从容器中删除给定的数据。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.DIAL" |
动作:拨打数据中指定的电话号码。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.EDIT" |
动作:为制定的数据显示可编辑界面。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.EMERGENCY_DIAL" |
动作:拨打紧急电话号码。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.LOGIN" |
动作:获取登录凭证。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.MAIN" |
动作:作为主入口点启动,不需要数据。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.PICK" |
动作:从数据中选择一个项目item,将被选中的项目返回。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.PICK_ACTIVITY" |
动作:选择一个activity,返回被选择的activity的类名 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.RUN" |
动作:运行数据(指定的应用),无论它(应用)是什么。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.SENDTO" |
动作:向 data 指定的接收者发送一个消息。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.GET_CONTENT" |
动作:让用户选择数据并返回。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.INSERT" |
动作:在容器中插入一个空项 (item)。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.SETTINGS" |
动作:显示系统设置。输入:无。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.VIEW" |
动作:向用户显示数据。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.WALLPAPER_SETTINGS" |
动作:显示选择墙纸的设置界面。输入:无。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.WEB_SEARCH" |
动作:执行 web 搜索。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.SYNC" |
动作:执行数据同步。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.SERVICE_STATE" |
广播:电话服务的状态已经改变。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.TIMEZONE_CHANGED" |
广播:时区已经改变。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.TIME_SET" |
广播:时间已经改变(重新设置)。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.TIME_TICK" |
广播:当前时间已经变化(正常的时间流逝)。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.UMS_CONNECTED" |
广播:设备进入 USB 大容量存储模式。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.UMS_DISCONNECTED" |
广播:设备从 USB 大容量存储模式退出。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.WALLPAPER_CHANGED" |
广播:系统的墙纸已经改变。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.XMPP_CONNECTED" |
广播:XMPP 连接已经被建立。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.XMPP_DI |
广播:XMPP 连接已经被断开。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.SIG_STR" |
广播:电话的信号强度已经改变。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.BATTERY_CHANGED" |
广播:充电状态,或者电池的电量发生变化。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED" |
广播:在系统启动后,这个动作被广播一次(只有一次) |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.DATA_ACTIVITY" |
广播:电话的数据活动(data activity)状态已经改变 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.DATA_STATE" |
广播:电话的数据连接状态已经改变。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.DATE_CHANGED" |
广播:日期被改变。 |
|
String |
"android.server.checkin.FOTA_CANCEL" |
广播:取消所有被挂起的 (pending) 更新下载。 |
|
String |
"android.server.checkin.FOTA_INSTALL" |
广播:更新已经被确认,马上就要开始安装。 |
|
String |
"android.server.checkin.FOTA_READY" |
广播:更新已经被下载,可以开始安装。 |
|
String |
"android.server.checkin.FOTA_RESTART" |
广播:恢复已经停止的更新下载。 |
|
String |
"android.server.checkin.FOTA_UPDATE" |
广播:通过 OTA 下载并安装操作系统更新。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.MEDIABUTTON" |
广播:用户按下了“Media Button”。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.MEDIA_BAD_REMOVAL" |
广播:扩展卡从SD卡插槽拔出,但是挂载点还没unmount。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.MEDIA_EJECT" |
广播:用户想要移除扩展介质(拔掉扩展卡)。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.MEDIA_MOUNTED" |
广播:扩展介质被插入,而且已经被挂载。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.MEDIA_REMOVED" |
广播:扩展介质被移除。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.MEDIA_SCANNER_FINISHED" |
广播:已经扫描完介质的一个目录。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.MEDIA_SCANNER_STARTED" |
广播:开始扫描介质的一个目录。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.MEDIA_SHARED" |
广播:扩展介质的挂载被解除 (unmount) |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.MEDIA_UNMOUNTED" |
广播:扩展介质存在,但是还没有被挂载 (mount)。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.MWI" |
广播:电话的消息等待(语音邮件)状态已经改变。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.PACKAGE_ADDED" |
广播:设备上新安装了一个应用程序包。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.PACKAGE_REMOVED" |
广播:设备上删除了一个应用程序包。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.PHONE_STATE" |
广播:电话状态已经改变。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.PROVIDER_CHANGED" |
广播:更新将要(真正)被安装。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.PROVISIONING_CHECK" |
广播:要求provisioning service下载最新的设置 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.SCREEN_OFF" |
广播:屏幕被关闭。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.SCREEN_ON" |
广播:屏幕已经被打开。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.NETWORK_TICKLE_RECEIVED" |
广播:设备收到了新的网络 "tickle" 通知。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.STATISTICS_REPORT" |
广播:要求 receivers 报告自己的统计信息。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.STATISTICS_STATE_CHANGED" |
广播:统计信息服务的状态已经改变。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.CFF" |
广播:语音电话的呼叫转移状态已经改变。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.action.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED" |
广播:设备的配置信息已经改变,参见 Resources.Configuration |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.ALTERNATIVE" |
类别:说明activity是用户正在浏的数据的一个可选操作。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.WALLPAPER" |
类别:这个 activity 能过为设备设置墙纸。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.UNIT_TEST" |
类别:应该被用作单元测试(通过 test harness 运行)。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.TEST" |
类别:作为测试目的使用,不是正常的用户体验的一部分。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.TAB" |
类别:activity应该在TabActivity中作为一个tab使用 |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.SAMPLE_CODE" |
类别:To be used as an sample code example (not part of the normal user experience). |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.PREFERENCE" |
类别:activity是一个设置面板 (preference panel)。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.HOME" |
类别:主屏幕 (activity),设备启动后显示的第一个 activity。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" |
类别:能够被浏览器安全使用的 activities 必须支持这个类别。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.DEFAULT" |
类别:如果 activity 是对数据执行确省动作(点击, center press)的一个选项,需要设置这个类别。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.DEVELOPMENT_PREFERENCE" |
类别:说明 activity 是一个设置面板 (development preference panel). |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.EMBED" |
类别:能够在上级(父)activity 中运行。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.category. |
类别:To be used as code under test for framework instrumentation tests. |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.GADGET" |
类别:这个 activity 可以被嵌入宿主 activity (activity that is hosting gadgets)。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" |
类别:Activity 应该被显示在顶级的 launcher 中。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.category.SELECTED_ALTERNATIVE" |
类别:对于被用户选中的数据,activity 是它的一个可选操作。 |
|
int |
8 0x00000008 |
启动标记:和 NEW_TASK_LAUNCH 联合使用,禁止将已有的任务改变为前景任务 (foreground)。 |
|
int |
4 0x00000004 |
启动标记:设置以后,activity 将成为历史堆栈中的第一个新任务(栈顶)。 |
|
int |
1 0x00000001 |
启动标记:设置以后,新的 activity 不会被保存在历史堆栈中。 |
|
int |
2 0x00000002 |
启动标记:设置以后,如果 activity 已经启动,而且位于历史堆栈的顶端,将不再启动(不重新启动) activity。 |
|
int |
16 0x00000010 |
启动标记:如果这个标记被设置,而且被一个已经存在的 activity 用来启动新的 activity,已有 activity 的回复目标 (reply target) 会被转移给新的 activity。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.extra.INTENT" |
附加数据:和 PICK_ACTIVITY_ACTION 一起使用时,说明用户选择的用来显示的 activity;和 ADD_SHORTCUT_ACTION 一起使用的时候,描述要添加的快捷方式。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.extra.LABEL" |
附加数据:大写字母开头的字符标签,和 ADD_SHORTCUT_ACTION 一起使用。 |
|
String |
"android.intent.extra.TEMPLATE" |
附加数据:新记录的初始化模板。 |
|
Creator |
无 |
无 |
